On Page Optimization in SEO
What is On-Page Optimization?
On-page optimization is the process of ensuring the content is both relevant and provides a great user experience. In the past, many businesses approached it as simply keyword stuffing; mentioning their keywords as many times as possible within the content. This made for a poor user experience.
Snippet is a programming term for a small region of re-usable source code, machine code, or text. Ordinarily, these are formally defined operative units to incorporate into larger programming modules. Snippet management is a feature of some text editors, program source code editors, IDEs, and related software. It allows the user to avoid repetitive typing in the course of routine edit operations.[1]
In On-Page Optimization, we can optimize a webpage easily by dividing it into two sections – Head section and Body section.
Head Section
Head section is optimized first. Head section consists of URL, title and meta description. At first, Google analyses its URL and check whether there is any hint about the website. After that it analyses the title.
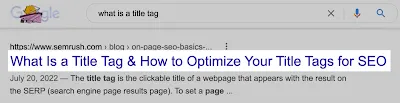
a) Title Optimization
<title>Write the Title</title>
Some of the factors that helps in title tag optimization is as follows:
• The title tag should be meaningful sentence including focusing keywords.
• Avoid spelling mistakes and grammatical errors.
• Title should be attractive and impressive.
• Title should contain minimum 3 words, otherwise it affects clarity.
• Pixel width of the title should be 512 pixel.
• Avoid using full capital letters because of limited pixel width.
• Avoid full small letters, which is less impressive.
• Character limitation is between 55 and 60 including space and special characters.
• Title should be unique for each webpage.
Similar title for different websites may lead to Cannibalism in which different websites compete for same title to rank on top.
• CTR (Click Through Rate) is the percentage of number of clicks per impressions in a website.
In case of irrelevant title tag, Google displays title as h1 tag from its body section in its snippet. Otherwise, Google will take h2 tag and so on.
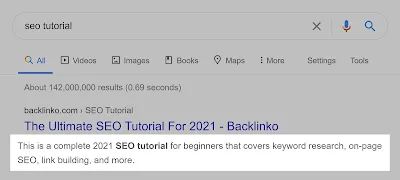
b) Meta Description
Meta description is the description or excerpt from a website that appears in the search results.
<meta name=”description” content=“Write the Description.”>
Factors affecting meta description tag are:
• Meta description must include focusing keywords.
• Avoid full capital letters.
• Avoid spelling mistakes and grammatical errors.
• It should be attractive.
• It should be unique for each webpage.
• There shouldn’t be any duplication.
• Pixel width of meta description should be 1024 pixel.
• Character limitation for a page is between 155 and 160.
• Character description for a blog or post should be under 150 because it also displays published date.
Modifying meta description helps in improving the website and thereby, increasing the CTR. If there is no relevant meta description or no meta description given, Google will show sentences from the content section of the body part, preferably the first sentence. Otherwise, it will take details from Open Directory Project to show meta tag. Open Directory Project is a completely free directory that is maintained by a community of volunteers.
Robots Meta Tag
Robots meta tag gives instructions to the bot that crawls a page whether to index or follow that page. It is one of the most important tag.
<meta name=”robots” content=”index,follow”/>
<meta name=”robots” content=”noindex,nofollow”/>
<meta name=”robots” content=”noimage”/>
The tag mentioned above tells the bot not to index images in webpage.
<meta name=”robots” content=”noodp”/>
This tag tells the bot not to use the description provided in open directory project. Being listed with the open directory can add value to websites.
<meta name=”robots” content=”noydir”/>
This tag tells the bot not to use the description provided in ydir (yahoo directory).
Keyword Meta Tag
<meta name=”keywords” content=”keywords”/>
This meta tag has importance during the time when Google introduced starter guide. This tag allows us to add keywords based on our site and tells search engines which keywords our page is optimized for. When web masters started misusing it by injecting keywords to get higher rank, Google stopped keyword meta tag for ranking purpose. It was officially declared to stop on September 21, 2009.
Body Section
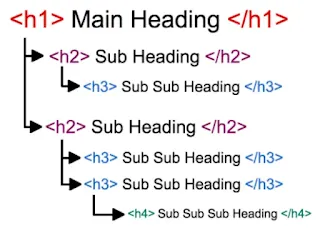
a) Header Tags
There are several header tags in html such as h1 (header 1), h2, h3, h4, h5 & h6. The most important part in the body section is the main heading. This most highlighted and large text is commonly h1 tag. H1 tag can have 7 to 8 words. It should be short and error free. There is more than one page in a website. It is better to use only one h1 tag in a landing page, which is a standalone webpage where users land when they click through an email, ad or link. Whereas, overview page contains all the information a user needs in a single page. If there is more than one h1 tag and are contrasting, it will lead to confusion while crawling a webpage. And Google store these pages in a temporary database called sand box. The problem is that the position of those pages won’t change or goes down even though it appears in search results.
H2 tag usually contains sub headings or it uses secondary keywords. But the content described should match the tag. In landing pages, one h2 tag is preferred. But in large articles, more than one h2 tag can be used. In case of h3 tag, more than two tags can be used.
b) Content Optimization
The content should reflect the topic. It should have relation with the heading which helps in clarity of a webpage for both Google and users. It is better to use focusing keywords in introductory sentences. Google prefers short and meaningful sentences. Lengthy sentences negatively affect comprehension and readability. If meta description is irrelevant, Google adds relevant sentences from the content section, preferably the first sentence.
c) Image Optimization
The image given should improve the quality of the page. If a user exits from a page immediately after seeing an irrelevant image and content, the trust value decreases and bounce rate increases. A webpage without any image will be less impressive. The image should educate people who visit the page. So quality image is needed.
Factors that help Google to identify an image include:
• Alt name
• File name
• The image provided should match the content of the page.
CDN stands for Content Delivery Network. The images uploaded in Blogger, WordPress, Facebook, etc., is saved in CDN. The benefit of CDN is that the images and media files uploaded can be delivered to users without affecting the functioning of the main server. So that, it can be accessed easily.
d) Anchor Text Optimization
Anchor text is the text which contains or adds hyperlink. It is the most visible portion in a content in Google. It boosts up the crawling process in Google. It also helps in understanding the topic of a page. Anchor text helps in getting more clicks which in turn results in more interaction. But overusing leads to passing the juice. The links which navigate to a page within the same website is referred to as internal links. Equity won’t be passed for internal links. Internal links help in internal navigation and it increases trust value. Trust value also increases when links are shared to sites with more trust value. Anchor text also helps in increased page views which in turn decreases bounce rate.
Keyword Density: It is the percentage of number of times a keyword appears in a webpage to the total word count in that page. But Google not considered it as a factor in ranking. But occurrence of focusing keywords two or three times will help in ranking. According to the Old School SEO Practice, focusing keywords can be written in bold. Using focusing keywords before a full stop or comma helps in better ranking. But it is not a factor for ranking according to Google.




Comments
Post a Comment